Before thinking about profit, a firm must first recover its costs. Break-even analysis helps answer this fundamental question in a clear and structured way.
Break-even analysis is widely used in cost accounting, budgeting, and financial planning. It shows the point at which total revenue equals total cost where there is no profit and no loss. While it is a powerful planning tool, it also has certain limitations that must be understood.
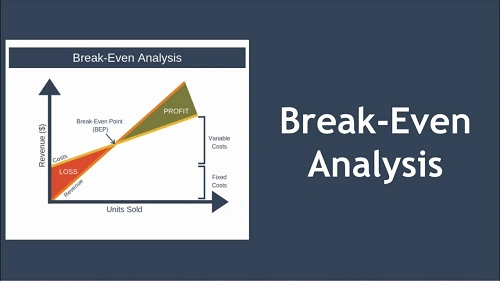
What Is Break-Even Analysis?
Break-even analysis is a financial technique used to determine the level of sales at which a business covers all its fixed and variable costs.
At the break-even point:
- Total cost = Total revenue
- Profit = 0
- Loss = 0
It helps management understand the relationship between cost, volume, and profit.
Advantages of Break-Even Analysis
1. Simple and Easy to Understand
One of the biggest advantages of break-even analysis is simplicity.
It:
- Uses basic cost and sales data
- Is easy to calculate and interpret
Even non-financial managers can understand it easily.
2. Helps in Profit Planning
Break-even analysis shows how much sales are needed to earn a desired profit.
Management can:
- Set sales targets
- Plan production levels
- Estimate profit at different sales volumes
This supports effective planning.
3. Useful for Cost Control
The analysis highlights cost structure.
It helps management:
- Identify fixed and variable costs
- Control unnecessary expenses
Understanding cost behavior improves cost management.
4. Assists in Pricing Decisions
Break-even analysis helps in fixing selling prices.
Management can:
- Analyze impact of price changes
- Decide minimum price to avoid loss
This is useful in competitive markets.
5. Supports Decision-Making
Break-even analysis assists in many business decisions.
It is useful for:
- Introducing a new product
- Expanding operations
- Choosing between alternatives
It provides a logical basis for decisions.
6. Shows Margin of Safety
Break-even analysis indicates the margin of safety.
This shows:
- How much sales can fall before losses begin
A higher margin of safety means lower business risk.
7. Useful for Startups and New Projects
For new businesses, break-even analysis is very helpful.
It helps:
- Assess feasibility
- Estimate time to reach no-loss stage
- Plan funding requirements
This reduces uncertainty in early stages.
Disadvantages of Break-Even Analysis
Despite its usefulness, break-even analysis has limitations.
1. Assumes Constant Costs and Prices
Break-even analysis assumes:
- Fixed costs remain constant
- Variable cost per unit is unchanged
- Selling price stays the same
In reality, costs and prices often change.
2. Ignores Demand and Market Conditions
The analysis focuses on cost and volume only.
It does not consider:
- Customer demand
- Competition
- Market trends
Reaching break-even sales may not always be practical.
3. Assumes All Output Is Sold
Break-even analysis assumes that:
- Whatever is produced is sold
This ignores inventory build-up and unsold stock.
4. Not Suitable for Multi-Product Firms
Break-even analysis becomes complex when:
- Multiple products are involved
- Sales mix keeps changing
Results may be misleading if product mix shifts.
5. Oversimplifies Business Reality
The analysis simplifies a complex business environment.
It ignores:
- Efficiency changes
- Learning curve effects
- Technological improvements
This reduces accuracy.
6. Short-Term Focus
Break-even analysis is more useful in the short run.
In the long run:
- Fixed costs may change
- Capacity may expand
This limits long-term applicability.
7. No Consideration of Time Value of Money
Break-even analysis does not consider:
- Timing of cash flows
- Time value of money
This can affect investment decisions.
When Break-Even Analysis Works Best
Break-even analysis is most effective when:
- Cost behavior is stable
- Business deals in a single product
- Used for short-term planning
- Combined with other financial tools
It should guide planning, not replace judgment.
Final Thoughts
Break-even analysis is a practical and powerful planning tool. It helps businesses understand cost structures, set sales targets, and evaluate risk. For startups and managers, it provides clarity on the minimum performance required to survive.
However, break-even analysis is not a complete decision-making tool. Its assumptions about costs, prices, and sales often differ from real-world conditions. Used alone, it can lead to overconfidence or wrong conclusions.
The real value of break-even analysis lies in awareness. When used alongside market analysis, budgeting, and managerial experience, it becomes a useful guide for smarter and more realistic business decisions.